Ports and Interface: The various port on the computer
allow it to communicate with the many different devices and peripherals
attached. The connectors on the back of your computer may also be called as
input / output ports ( i/o ports ) or communication ports.
The first
thing to know is the different between a male and female connector. The male
connector fits inside the female connector. If the connector has pins
protruding from it, it’s a male connector. If the connector has holes for the
pins to fit into, then it’s a female connector.
The second
thing you should remember is that when you join a connector to a port, they
must have the same shape and the same number of pins or holes.
The various
I/O ports are Serial, Parallel, PS/2, USB & firewire port. Out of the I/O
ports mentioned except the USB and firewire ports, the other ports are not hot
swappable. USB and Firewire ports are the only ports that should be considered
hot-swappable ( this means they can be plugged in or unplugged while the
machine is on ).
External
ports ( which are linked to the motherboard ) allow users to connect devices
such as scanner, printers, mice and keyboards.
Serial: A serial port can be used to connect
many types of devices. Data is transferred to and from the device one bit at a
time.
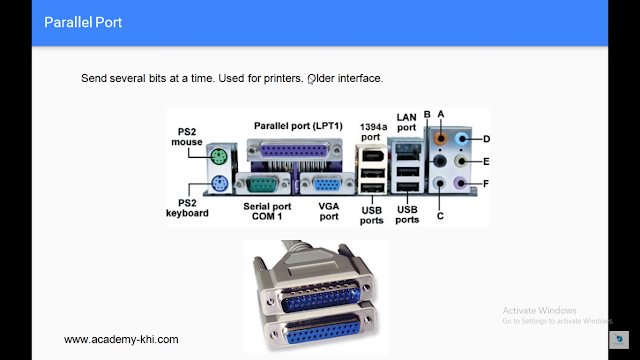
Parallel: A parallel port usually has a 25-pin
connector and is most often used to connect local printers. Devices attached to
a parallel port are capable of receiving more than one bit of data at a time.
PS/2: PS/2 ports are used to connect the
mouse and the keyboard.
Serial and
parallel ports are currently considered to be “legacy ports” since they use old
technology for data transfer. Never technology includes the following.
Serial and
parallel ports are currently considered to be “legacy ports”. Since they use
old technology for data transfer. Newer technology includes the following:
USB
1.1 – USB Basic Speed: USB (Universal Serial Bus )is an external bus standard that
supports data transfer rates of 12 Mbps (12 million bits per seconds). A single
USB port can be used to connect up to 127 peripheral devices, such as mice,
modems, and keyboard. USB also supports plug and play installation and “hot
plugging”, meaning you do not have to shut down the computer in order to attach
or detach a device from the machine.
USB 2.0 – USB Hi-Speed: USB 2.0 is a new version of the USB
specification. This new port is backwards-compatible, allowing older USB 1.1
devices to connect and update without trouble. However, the new USB Hi-Speed
ports support data transfer rates of 480 Mbps, even faster than FireWire ports.
USB 3.0 – USB SuperSpeed: USB 3.0 defines a new SuperSpeed
transfer mode, with associated new backwards-compatible plugs, receptacles, and
cables.
The new
SuperSpeed mode provides a data signaling rate of 5 Gbit/s and the
specification considers it reasonable to achieve only around 3.2 Gbit/s (0.4
GB/s or 400 MB/s)
FireWire: FireWire is a very fast external bus
standard that supports data transfer rates of up to 400 Mbps. FireWire is also
known as IEEE 1394. A single 1394 port can be used to connect up to 63 external
devices and is much faster than USB 1.1. it supports both plug and play and hot
plugging and also provides power to peripheral devices.
COM and LPT Assignments
Port
|
I/O
Address
|
IRQ
|
COM 1
|
3F8
|
4
|
COM 2
|
2F8
|
3
|
LPT1
|
378
|
7
|
LPT2
|
278
|
5
|
Asynchronous and Synchronous
communication
There are
two schemes of transmitting data to be ports.
Asynchronous
Synchronous
In the
asynchronous scheme, each character is transmitted with the start bit and the
stop bit as the synchronization bits.
In the
synchronous scheme, a bit pattern called sync is transmitted after a fixed
number of data bytes.
Asynchronous
communication is generally used with slow peripherals, whereas very high speed
transmission is possible with the synchronous communication scheme.
Serial Interface: PC support two serial interfaces
Each is an RS-232 standard interface. The PC supports asynchronous and
synchronous communication. Synchronous communication is rarely used, it is used
only for high speed communication between PC’s. Asynchronous communication is
widely used in PCs.
The RS232 Serial Interface: The RS-232 interface is a standard
interface specified by the Electronic Industries Association ( EIA ) and is
followed by the manufacturers of computers and data communication products ( RS
stands for Recommended Standard ). RS-232 was basically designed to allow
computing devices called equipment (DTE) to talk to communications devices
called data circuit-terminatting equipment (DCE). So there is a DTE-type RS-232
interface and a DCE-type RS-232 interface. RS-232 is designed to allow DTEs to
talk only to DCEs. Rs-232 used DB25 and DB9 connectors. Male connectors go on
the DTEs; female connectors go on the DCEs.
Parallel (
Centronics ) Interfaces/IEEE 1284
The most
common method of attaching a printer to a computer is through a simple
interface called the Centronics interface. The original parallel ports had
eight outputs, five input and four bidirectional lines. A parallel ports transfer multiple bits at
once, while a serial ports transfer a bit at a time. Pc can support up to three
parallel ports. They are named LPT1 ,LPT2 and LPT3; the name refers to Line
Printer 1 2 and 3.
PS/2 port:
This port was designed by IBM for their Personal System /2 computers. The PS/2 port
has lived on in other computers as the standard for keyboard and mice. Most
computers come with two PS/2 ports.
USB (
Universal Serial Bus ): USB s peripheral bus standard developed by PC and
telecom industry leaders – Compaq, DEC,
IBM etc that brings plug and play of computer slots and reconfigure the system.
Personal computer equipped with USB
allows computer peripherals to be automatically configured as soon as they are
physically attached – without the need to reboot or run setup. USB also allow
multiple devices – up to 127 – to run simultaneously on a computer, with
peripheral such as monitors and keyboards acting as additional plug – in sites,
or hubs.
Digital Visual Interface: Digital Visual Interface ( DVI )
is a video display interface developed
by the Digital Display Working Group ( DDWG ). The digital interface is used to
connect to a video source, such as a video display controller to a display device,
such as a computer monitor.
Display Port: Display Port is a digital display
interface developed by the Video Electronics Standards Association ( VESA ) the
interface is primarily used to connect a video source to a display device such
as a computer monitor, though it can also be used to carry audio, USB, and
other forms of data.
Video Graphics Array: A Video Graphics Array ( VGA )
connector is a three-row 15-pin DE-15 connector. The 15-pin VGA connector was
provided on many video cars, computer monitors, laptop computers, projectors,
and high definition television sets. On laptop computers or other small
devices, a mini-VGA port was sometimes used in place of the full-sized VGA
connector.
SCSI ( Small Computer System
Interface ) Basics: SCSI
is a set of ANSI standard electronic interfaces that allow personal computers
to communicate with peripheral hardware such as disk drives, tape drives, CD –
ROM drives, printers and scanners faster and more flexibly than previous
interface.





No comments:
Post a Comment